|
|
||
|
||
|
Privacy Policy | Editorial Policy | Profit Policy | Join the Association | List of Members | Contact us | Index | Links |
||
|
Back Go to page: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Forward |
||
|
Contents.
Does HTTPS make the Internet secure? The Garage Girls and their WW2 secret.
|
||
|
|
||
|
Browser Security Myths that need busting.
Misinformation or outdated advice about online security can make you and your personal data vulnerable so let’s look at five common browser security myths so you can keep your understanding of browser security and the browser itself up to date together.
Incognito Mode makes you completely anonymous
The myth that incognito or private browsing mode makes you completely anonymous is a common misconception. Incognito mode provides privacy by not storing your search history, cookies, or form data, however, this only applies to your particular device and browser.
Your internet service provider (ISP), network administrator and the websites you visit can still track your activities while in this mode. Also, if malware lurks on your device, incognito mode won’t hide your activities from it. For more robust privacy, you might consider using a VPN or a privacy-focused browser like Tor, though these tools also have limitations that we will discuss later.
A secure website (HTTPS) means it’s safe to browse.
Most internet users have been taught to trust websites that use HTTPS, indicated by a padlock symbol in the browser’s address bar. It’s true that HTTPS encrypts your communication with the website, which prevents snoopers from reading the data in transit. However, this does not guarantee that the website itself is safe. HTTPS only ensures secure transmission of data; it does not ensure the integrity of the site’s content. Cybercriminals can also use HTTPS on their malicious sites, tricking visitors into thinking these sites are safe. Always ensure the website you’re visiting is genuine and reputable, regardless of whether it uses HTTPS.
Downloading files is the only way to get Malware.
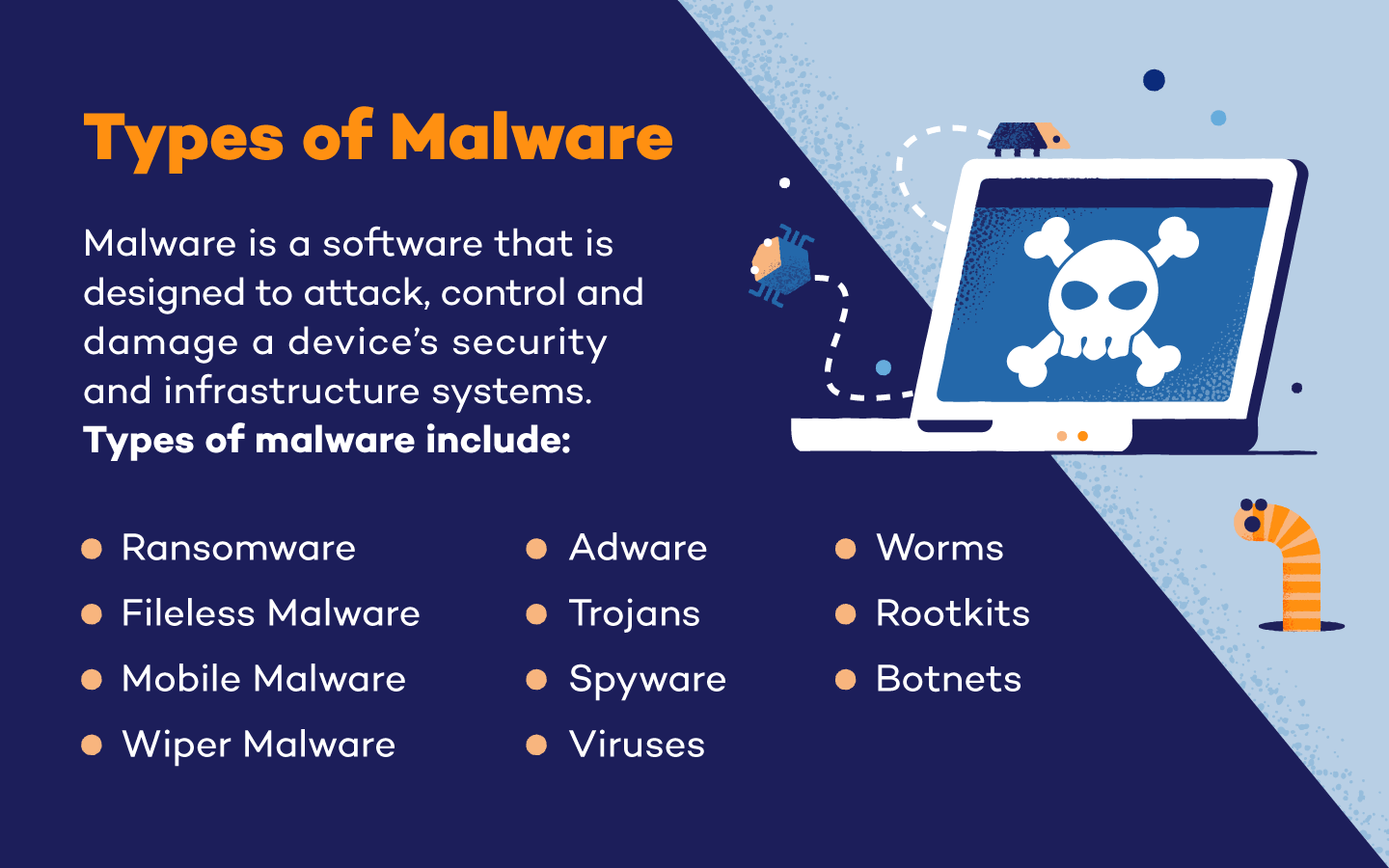
Many people believe that they can only get malware by downloading and running suspicious files. While this is one way to get infected, it’s not the only way. Drive-by downloads and malicious advertisements can infect your computer without requiring you to download and run a file manually.
You can also get infected by simply visiting a compromised website, even without clicking on anything. Always keep your browser and its plugins updated to the latest version to guard against known vulnerabilities and consider using a reputable ad blocker to minimize risks.
|
||
|
|
||
|
HTTPS is almost everywhere. So why isn't the Internet secure now?
Most web traffic online is now sent over an HTTPS connection, making it "secure." In fact, Google now warns that unencrypted HTTP sites are "Not Secure." So why is there still so much malware, phishing, and other dangerous activity online?
"Secure" Sites just have a Secure Connection.
|
||
|
|
||
|
Chrome used to display the word "Secure" and a green padlock in the address bar when you were visiting a website using HTTPS. Modern versions of Chrome simple have a little gray lock icon here, without the word "Secure."
That's partly because HTTPS is now considered the new baseline standard. Everything should be secure by default, so Chrome only warns you that a connection is "Not Secure" when you're accessing a site over an HTTP connection, however, the word "Secure" is also gone because it was a little misleading. It sounds like Chrome is vouching for the contents of the site as if everything on this page is "secure," but that's not true at all. A "secure" HTTPS site could be filled with malware or could be a fake phishing site.
HTTPS stops Snooping and Tampering.
HTTPS is great, but it doesn't just make everything secure. HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. It's like the standard HTTP protocol for connecting to websites, but with a layer of secure encryption.
|
||
|
|
||
|
This encryption prevents people from snooping on your data in transit and it stops man-in-the-middle attacks that can modify the website as it's sent to you. For example, no one can snoop on payment details you send to the website.
In short, HTTPS ensures the connection between you and that particular website is secure. No one can eavesdrop or tamper with it. That's it.
This doesn't really mean a Site is "Secure"
|
||
|
|
||
|
HTTPS is great, and all websites should use it, however, all it means is you're using a secure connection with that particular website. The word "Secure" doesn't say anything about the contents of that website. All it means is the website operator has purchased a certificate and set up encryption to secure the connection.
For example, a dangerous website full of malicious downloads might be delivered via HTTPS. All that means is the website and the files you download are sent over a secure connection, but they might not be secure. Similarly, a criminal could buy a domain like "bankoamerica.com," get an SSL encryption certificate for it and imitate Bank of America's real website. This would be a phishing site with the "secure" padlock, but all that means is you have a secure connection to that phishing site.
HTTPS is still great.
HTTPS sites aren't really "secure." Websites switching to HTTPS helps solve some problems, but it doesn't end the scourge of malware, phishing, spam, attacks on vulnerable sites, or various other scams online. The shift toward HTTPs is still great for the internet! According to Google's statistics, 80% of web pages loaded in Chrome on Windows are loaded over HTTPS and Chrome users on Windows spend 88% of their browsing time on HTTPS sites.
This transition does make it harder for criminals to eavesdrop on personal data, especially on public Wi-Fi or other public networks. It also greatly minimizes the odds that you'll encounter a man-in-the-middle attack on public Wi-Fi or another network. For example, let's say you're downloading a program's .exe file from a website while you're connected to a public Wi-Fi network. If you're connected with HTTP, the Wi-FI operator could tamper with the download and send you a different, malicious .exe file. If you're connected with HTTPS, the connection is secure, and no one can tamper with your software download.
That's a huge win! But it's no silver bullet. You still need to use basic online safety practices to protect yourself from malware, spot phishing sites, and avoid other online problems.
|
||
|
If you think you are smarter than the previous generation, 50 years ago the owner's manual of a car showed you how to adjust the valve tappets. Today it warns you not to drink the contents of the battery. |
||
|
|
||
|
The Garage Girls and their secret war machine.
In a suburban Brisbane garage, young women decoded radio transmissions that changed the course of World War II. For the first time, their top-secret work on a panicked Japanese cable about a new type of weapon can be revealed.
Not long after an American atomic bomb exploded over Hiroshima, a horrified Japanese officer radioed back to Imperial Navy headquarters in Tokyo to report what he had witnessed. The tone of the officer’s report didn’t seem to particularly reflect the constrained emotion one might expect of a buttoned-up Japanese man of war. But that day, the 6th August 1945, his extraordinary witness account was intercepted by an Australian signalman stationed near the Philippines.
From there, it passed into the hands of a secret unit of women codebreakers whose work in a garage at the back of a Brisbane mansion (21 Henry St, Ascot) was kept top secret for decades. The never before released cable, declassified for the ABC by the Australian Signals Directorate, was decrypted, revealing the Japanese officer’s account of what happened when three B-29s flew over Hiroshima that morning.
It was one of first reports of the apocalyptic destruction that would soon become familiar around the world. “A terrific explosion accompanied by flame and smoke occurred at an altitude of 500 to 600 metres. The concussion was beyond imagination and demolished practically every house in the city,” his cable read. “About 80 per cent of the city was wiped out, destroyed or burnt. Only a portion of the western section escaped the disaster. Casualties have been estimated at 100,000 persons.”
The officer concluded his message with these chilling words: “Please investigate and report any information concerning this new type of bomb.”
The Garage Girls and their secret war machine
Thousands of kilometres away, Central Bureau was a top-secret intelligence agency hiding in plain sight. It was given a beige name to disguise its thorny work handling the most sensitive military communications and inside were young Australian women who had heeded the call and stepped into a world of interception and intrigue that they could have barely imagined.
|
||
|
|
||
|
Joyce Grace and Joan Eldred at work at the draper C. Winn in Ashfield in 1940.
Joyce Grace was a 19-year-old working in a Sydney haberdashery store in 1943 when she received a letter from the Manpower Directorate, an agency of the Australian government tasked with conscripting civilians to fill labour shortages in the latter half of World War II.
“The letter said that I wasn’t working in an essential industry,” Joyce told the ABC. “And they put it to me that if I left my job, the boss would have to take me back and give me the exact same job that I had when I left him. Joyce was sent for six weeks’ basic military training at Ingleburn Army Camp where she was asked what type of army work took her interest.
“I hadn’t given much thought to what I might do, but anyhow, I said, ‘Well, my father was a naval signalman in the First World War, and he seemed to enjoy the job — I’ll give signals a go’.”.
Joyce Grace was dispatched to Bonegilla near the Victoria-NSW border for a signals course, training in morse code and wireless messaging. It was here that she met lifelong friend Coral Hinds. “My friend Joy,” Coral remembers wistfully. “She was tall, her hair was straight, a no-nonsense person. Joy and I seemed to just migrate together into doing things and look, we’ve been friends all these years.”
Coral left school at 14 and worked in a cake shop and then a grocer’s. Not having a brother old enough to serve in the war, Coral and her younger sister Ruth decided to join up instead. Shortly after turning 18, Coral enlisted in the Australian Women’s Army Service (AWAS). “The boss wasn’t very happy about it. But that didn’t make any difference — I still went,” she said.
After Bonegilla and then a stint in Melbourne for more intense training in communications, Coral and Joyce were put on a train to Brisbane. Their new place of work was at 21 Henry Street, Ascot, in a hot garage at the back of Nyrambla, an impressive 1880s mansion.
|
||
|
|
||
|
The entrance to Nyrambla in Ascot, Brisbane, suburban mansion turned war base. From left, Joyce Grace, Helen Kenny and Betty Paterson approaching the guard.
Nyrambla had been requisitioned by United States General Douglas MacArthur, the Allies’ supreme commander in the south-west Pacific, for his headquarters. “That’s how I became a Garage Girl,” chuckles Joyce.
Inside the Central Bureau.
Joyce and Coral found themselves working in the cipher unit of Central Bureau, a signals intelligence organisation tasked with decrypting intercepted messages from the Imperial Japanese Army. “Everything was so secret. ‘Don’t talk about it outside. Don’t tell anybody. You can tell them you’re in signals, but don’t go any further than that’. And we sort of knew that there was something special about it,” Joyce says. “You couldn’t talk about it,” Coral recalls. “See, mum and dad didn’t know what I did. I used to just tell people I was in signals. So, you know, it really just gets a way of life.”
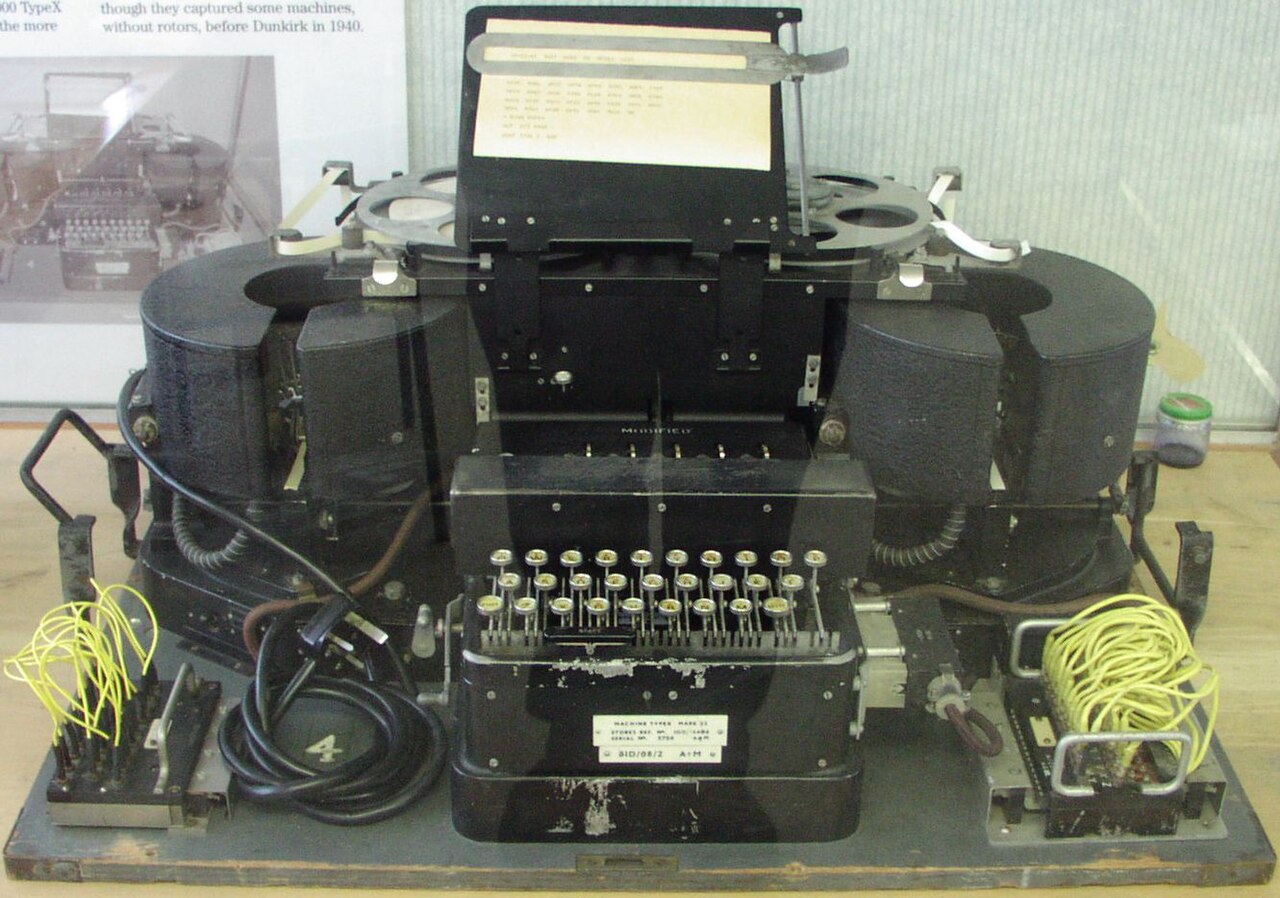
Working around-the-clock in eight-hour shifts, the Garage Girls used 12 British-made TypeX coding machines to both decode and encrypt highly classified material. The Japanese signals were in Kana, or syllabic characters, which meant that once intercepted messages were decrypted, they still had to be translated into English by Central Bureau linguists. If the TypeX machine was not generating recognisable Japanese syllables, the Garage Girls knew that the rotors in the machine, which were key to decryption, likely needed adjustment. “On the whole, you just got to and plonked away on the TypeX and if it didn’t work you stayed there and fiddled around with it until it did work,” Coral explains.
|
||
|
|
||
|
“It was our secret machine,” Joyce says of the TypeX.
“You had to set them up, before you could sit down and type, whether you’re going to type for a message to be decoded, or when you’re going to encode a message and the machine did either one of those things.”
Love and war.
Despite spending the war in a repurposed suburban house, for the Garage Girls the experience was far removed from their pre-war lives working in shops or going to school. Some moved away from home for the first time for basic training and enjoyed the camaraderie and shore leave that came with their freedom and of course, for many that led to finding love.
The Garage Girls had developed a technique called “padding”, where messages were lengthened with scraps of irrelevant information to confuse the enemy. “If you had the message too short, it was easy for them to work it out,” Coral explains. “But by putting this padding on … it just put the enemy off the scent.” It also had the side effect of letting them pass messages to friends and lovers far from home.
Coral met her husband Sandy Hinds at Central Bureau. He was a signaller and was waiting to be sent north to New Guinea. “Meeting Sandy, that was the most important thing in my life,” she says. “I met him in the May, he went away in the June and in the October, the 20th October 1944, he asked me to marry him. A faint heart never won a fair lady, somebody said.” Sandy and Coral eventually got married on June 2, 1945.
|
||
|
|
||
|
Sandy Hind’s and Coral Osborne wedding in 1945.
But during the war, Coral fell ill during Sandy’s deployment and the Garage Girls were keen to tell him how she was faring by using the TypeX machine. When Coral ended up in hospital, Joyce decided to get a message to Sandy in the jungle. “I made it short, but it was just to let Sandy know that Coral was doing alright, she was coming out of hospital. “Well, Sandy got that little message that I sent and he carried it around with him I believe for a long time.”
Taking down an admiral.
The work of Central Bureau contributed to one of the big strategic strikes against Japan in April 1943: Operation Vengeance.
|
||
|
|
||
|
Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto, the commander of the Imperial Japanese Navy, was architect of the December 1941 Pearl Harbour attack, making him a top military target for Washington.
An Australian wireless unit picked up Japanese radio signals which, when decrypted, revealed that Yamamoto would be visiting troops in the Solomon Islands and New Guinea. The Japanese cable not only detailed the admiral’s itinerary, but also the type of Mitsubishi Betty bombers he and his officers would be flying in, as well as the six Mitsubishi Zero fighters that would be accompanying them. “They had everything, the whole lot,” Joyce says. “And sure enough, they were waiting for him, our boys, and the Americans, and they got him.” US fighter planes intercepted Yamamoto’s plane over Bougainville, downing it on April 18, 1943. “They shot the big boy down,” Coral says. “Oh, it was quite a thrill.”
|
||
|
|
||
|
The wreckage of Yamamoto’s plane still rusts in the jungle about 9 kilometres from the Panguna copper mine in PNG.
The admiral’s death was a blow to Japanese morale but it would be another two and a half years before the war in the Pacific ended.
A chance discovery.
The Allies had been split over the strategic wisdom of Operation Vengeance; the British believed that in exacting revenge against Yamamoto, the US had risked revealing their joint code-breaking ability which had broader strategic value. Decoding Japanese signals had proven valuable in the war against Germany, insofar as Japanese diplomatic cables from Europe helped inform the Allies of Germany’s evolving military strategy. While the Allies’ ability to decode encrypted Japanese signals had steadily improved, it was aided immeasurably by an Australian sapper’s chance discovery of a steel trunk buried in soggy ground by retreating Japanese troops in January 1944 at Sio in New Guinea.
The trunk contained sodden code books from the Japanese 20th Army division. Dispatched back to Central Bureau, the code books were carefully prised apart, page by page and then dried on clothes lines and heaters. Joyce remembers her friend Helen Kenny, a fellow Garage Girl, helping in that delicate operation. (Kenny later had a long and successful career in journalism, including as literary editor for the Sydney Morning Herald.) But with the Japanese code books now photographed and distributed among Allied codebreakers the enemy’s signals were terribly compromised, they could be decoded and read by Allied intelligence almost as quickly as the Japanese received it themselves. When a Japanese officer sent his grim cable from the port of Kure, south-east of Hiroshima, to Tokyo headquarters on August 6, 1945, it was able to be decoded almost word-for-word.
Seeing the message
Joyce and Coral, like the rest of the Garage Girls, did not speak Japanese, so the first time they saw the translated Hiroshima cable was when the ABC showed it to them. (Click it to get a bigger view)
The translated Hiroshima cable was declassified for the ABC documentary Breaking the Code: Cyber Secrets Revealed. Joyce was struck particularly by the cable’s last line: Please investigate and report any information concerning this new type of bomb.
“I don’t like the sound of it,” Joyce says, adding that the first she’d known about the atomic bomb was when she read it in the newspapers. “I was shocked. Horrible. Terrible business.” Coral says she too finds the nuclear attack on Hiroshima too confronting to consider. “I know it was dreadful. But if it hadn’t been them, it would’ve been us. I know it sounds dreadful but, I mean, when I think of what they did to our servicemen, the dreadful lives that they ended up with because of their cruelty…”
Coral doesn’t quite finish the sentence. Instead, she starts another: “Yes, well, see they tried to kill our boys off in prisoner of war camps and some of them are still paying for it. “I suppose we felt sorry for the Japanese, for the ordinary people, but you know, when you think some of the things that they did to our POWs and things … it was just a blessing when it was all over.”
And, according to the American general at Nyrambla, the work of the Garage Girls significantly shortened hostilities in the Pacific. “Douglas MacArthur, I think it was, that put the news out that we reduced the war time by two years with the work that we had done, so we must have done something special and I feel very proud about it,” Joyce Grace says.
The lesson in war?
“Keep it peaceful,” Joyce concludes. “Help to keep it peaceful, if you can. Do whatever you can. War’s terrible.”
Recognition.
|
||
|
|
||
|
Joyce Grace received the Australian Intelligence Medal from Governor-General David Hurley in April 2023
Coral Hinds, Joyce Grace and Ailsa Hale, the last surviving Garage Girls, were awarded the Australian Intelligence Medal in January 2023. Coral died on the 10th February, 2023, Joyce Grace turned 100 on the 4th March 2023. She and Coral Hinds’s son Anthony were presented their medals by the Governor-General on the 18th April 2023.
The story of the Garage Girls was featured in ABC TV’s documentary Breaking the Code: Cyber Secrets Revealed on News Channel, on the 4th June and on ABC1 on the 5th June.
You can see it here https://iview.abc.net.au/video/NS2337H001S00
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
Back Go to page: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Forward |
||